Cultural Heritage Protection
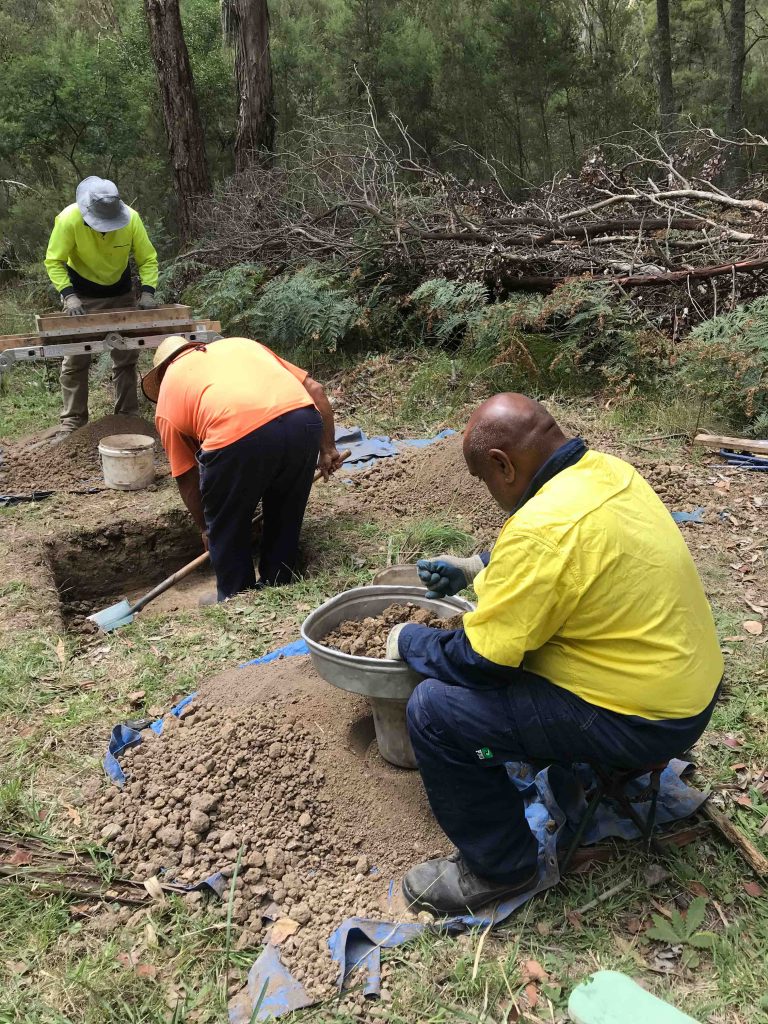
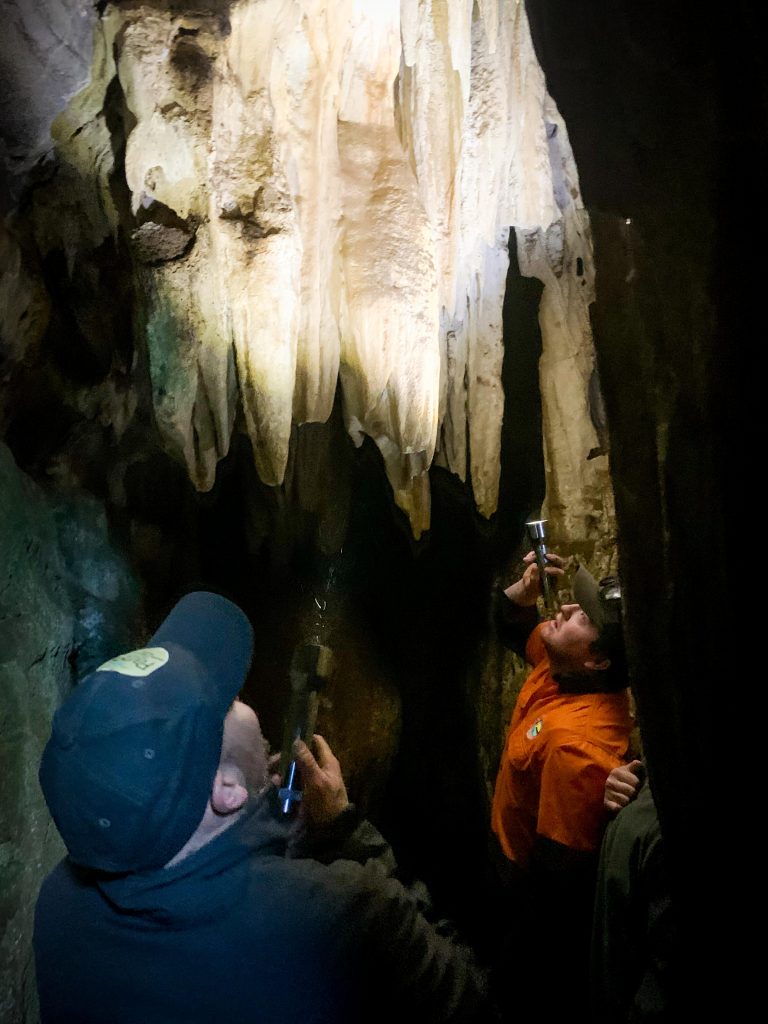
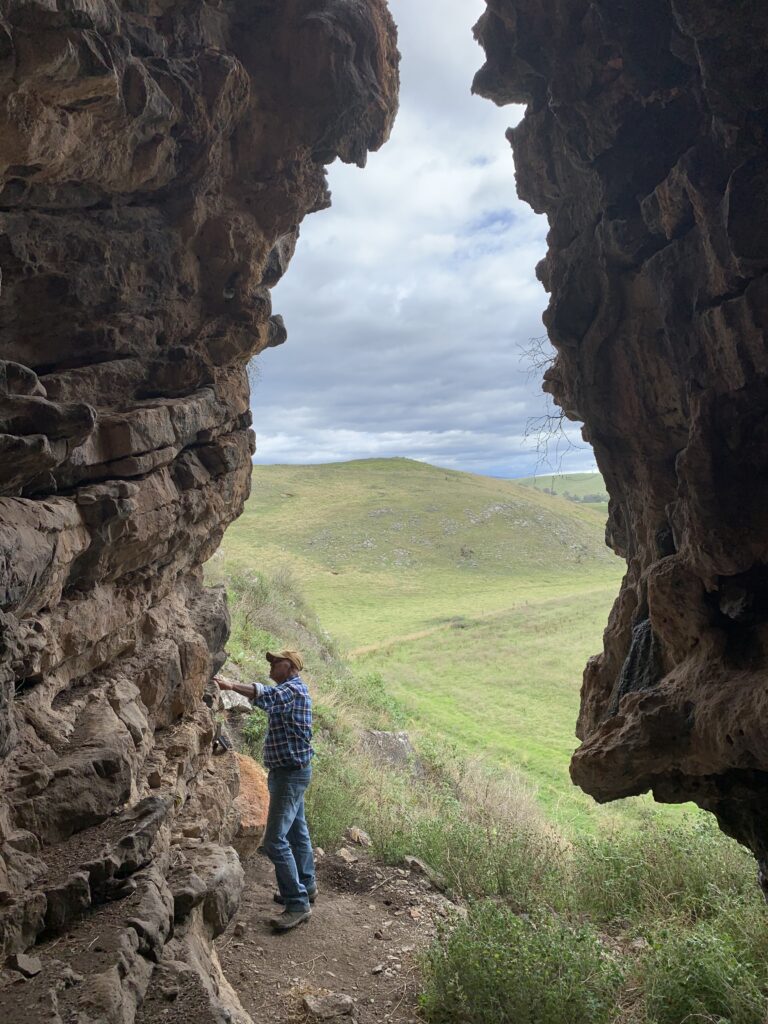
Our heritage is strong across our landscape, and Aboriginal cultural sites and artefacts can be found along our songlines, and trade routes, mountain ridges and waterways. They remind us about the ways of our Ancestors and show our close and continuing connection to Country.
– Gunaikurnai Whole of Country Plan
Some of these sites have been recorded, however many have not yet been found and protected. Our spiritual connection is something that cannot be seen, but nevertheless exists strongly in the places we walk and in the paths of our ancestors.
As a Registered Aboriginal Party (RAP) under the Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Act 2006, GLaWAC is the primary source of advice and knowledge for the Victorian
Government on matters relating to Aboriginal places located in or Aboriginal objects originating from our area.
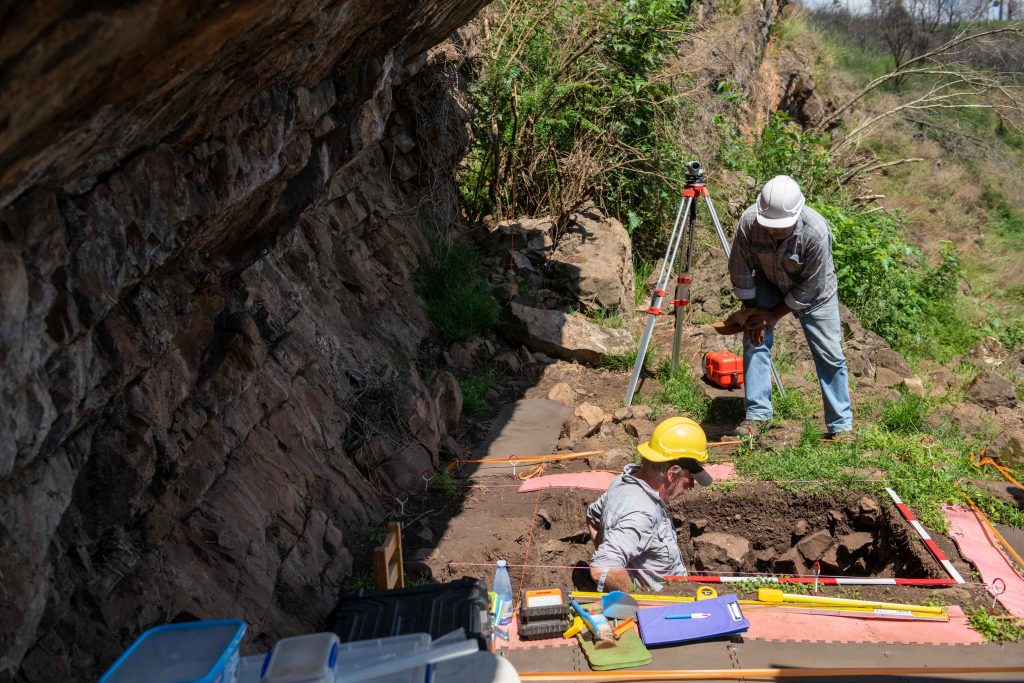
The GLaWAC RAP Team administers a process for Gunaikurnai Traditional Owners to protect our cultural heritage within the Gunaikurnai RAP area and to comment on the protection of Aboriginal cultural heritage within adjacent non-RAP areas.
What areas are included within the Gunaikurnai RAP boundary?
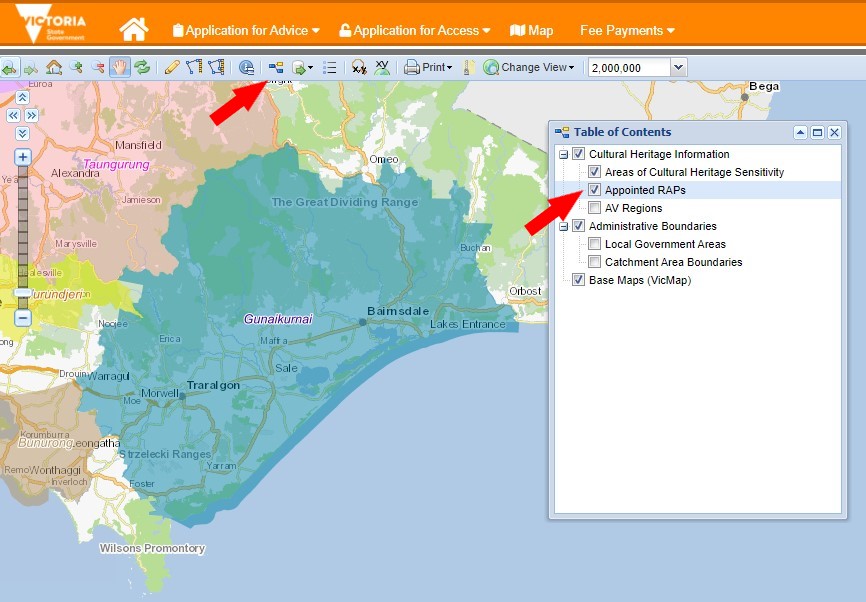
If you’d like to see an interactive map of the GLaWAC RAP area, you can explore this map online:
Interactive Map
Click on the layers section in the toolbar and in the drop-down contents box, tick the box titled “Appointed RAPs”(see arrows in the screenshot below). You will now be able to explore the GLaWAC RAP area!
What is the Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Act 2006 about?
The Aboriginal Heritage Act 2006 (the Act) acts primarily to provide for the protection of Aboriginal cultural heritage in Victoria.
– The Act allows different organisations, groups and bodies to connect and better enforce and preserve policies regarding Aboriginal Heritage. It does this through:
– The Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Council provides a state-wide voice for Aboriginal people and advises the Minister for Aboriginal Affairs on cultural heritage management.
– Registered Aboriginal Parties allow Aboriginal groups with connections to Country to be involved in cultural heritage decision making.
– The Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Register records details about Aboriginal places, objects, and knowledge.
– Cultural Heritage Management Plans (CHMPs) and Cultural Heritage Permit processes, to manage activities that may impact Aboriginal cultural heritage.
– Providing sanctions and penalties to prevent harm to Aboriginal cultural heritage.
– Powers for Authorised Officers and Aboriginal Heritage Officers, and increased fees and charges for breaches of the Act.
– Applying financial penalty’s for harming cultural heritage, unintentionally or otherwise
To find out more about the Aboriginal Heritage Act 2006, please click here
How do I know if I need a Cultural Heritage Management Plan or Cultural Heritage Permit?
Before starting any development activities it’s important you understand if it could affect Aboriginal cultural heritage. That way, your development can proceed smoothly without costly interruptions.
To find out more about the requirements for managing and protecting Aboriginal cultural heritage, please click here
Cultural Heritage Booking Form
GLaWAC has updated the way we deliver and manage our Cultural Heritage services. We continue to participate in the preparation of Cultural Heritage Management Plans (CHMPs), evaluate plans prepared by Cultural Heritage Advisors, advise State and Local Governments on Cultural Heritage Permit applications, negotiate Cultural Heritage Agreements, and support the repatriation of Aboriginal cultural heritage.
Bookings for these services must now be made through our online booking system. This new process allows you to select the type of service you need and choose a suitable date and time for your meeting or assessment.
To make a booking, please click the button below and complete the required information.
If you experience any issues with the booking system or are unsure which service to select, please contact us at admin@glawac.com.au for assistance.
Take a listen to GLaWAC RAP Team talking about the importance of preserving and recording the cultural heritage of our people.









